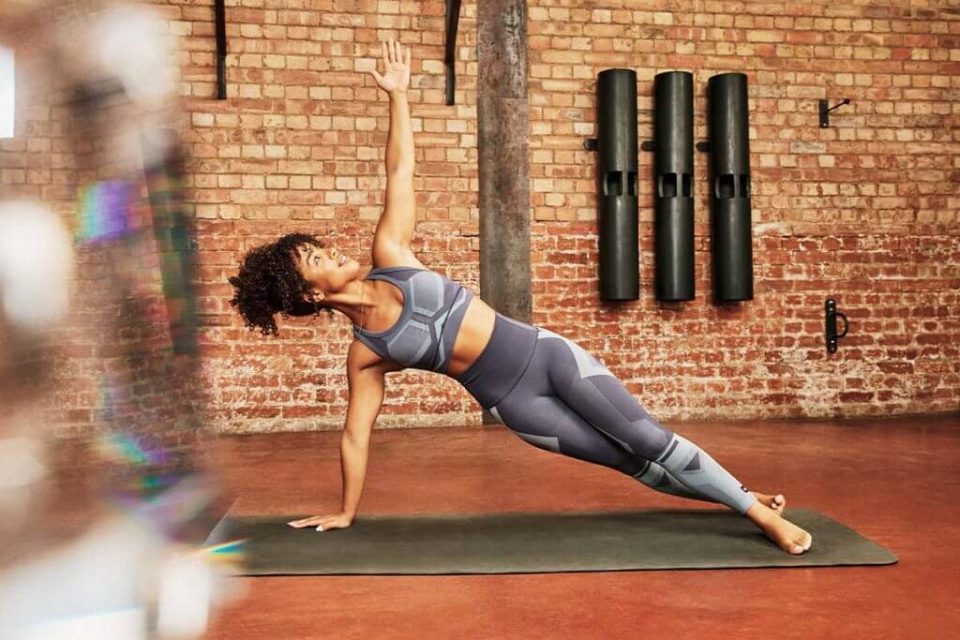
The body is built to move, so most exercise is healthy and beneficial. Yoga is one of the least intense and most unique forms of fitness. Many potential or current yogis ask: “Can you get fit and toned from yoga?” Here, we explore how yoga helps you stay fit.
1. Yoga for Fitness: A Yoga Workout
While yoga alone can help someone get in shape, this is highly dependent on your current fitness level, the style of yoga, and the intensity or frequency of yoga sessions.
Launching A Fitness Lifestyle
Yoga is a great way to launch a fitness journey, especially if you’re new to exercise or out-of-shape. Yoga activates and exercises every muscle in the body, burning calories and strengthening muscles. Someone new to yoga or exercise may see noticeable changes within weeks, no matter the type or intensity of yoga.
Practice doesn’t make perfect; practice makes flow.
And that’s what the new Discover Yoga Series on the adidas Training app is all about: bringing you to your flow state. Perfection doesn’t matter: whether you’re new to the practice or a seasoned yogi, our 8-week series puts you on the path to grace, mobility, and bliss. From pranayama to vinyasa, OM to namaste, our professional yoga instructor leads you through every pose. All you need is a mat, a sense of curiosity, and a desire to get stronger, from the inside out. Get your flow on!
Yoga For Strength or Aerobic Training
Those who regularly work out may also notice changes in their fitness when practicing yoga, especially if they set clear goals for their practice. People who regularly strength-train should do cardio yoga versus runners who can do yoga to increase strength. Here are more details on what kind of yoga to do and why:
- Bikram yoga is a challenging style of yoga done in a sweltering room. It has been proven to help people increase the weight that they could deadlift.(1) And, it might help with cardiovascular wellness because of heart rate elevation due to heat.
- Yoga that involves holding challenging poses for a long time will increase strength. Staying in a pose until you feel muscle fatigue is the key to building more muscle. Styles like Ashtanga and Power yoga naturally integrate these kinds of isometric contractions.
- Fast-flowing styles of yoga, like Vinyasa yoga, can boost cardiovascular endurance and strength. First, learn a series of poses and then link them together (typically, one breath, one movement). Beware: certain yoga poses are dangerous when linked improperly in a flow. It’s best to learn a yoga flow from trained practitioners.
Older adults are especially likely to gain cardiovascular benefits from yoga(2). So invite Grandma to join you! And even if you do not see a marked increase in your running splits, yoga is proven to improve overall cardiovascular health.(3) Your lungs will feel healthier!
Yoga For Flexibility
While being flexible will not help you lose weight or build muscle, it is a measure of fitness and physical health. One study showed that a regular yoga practice increased the flexibility of computer users specifically. Even a simple and short chair yoga session can make you more flexible, especially when you do it frequently.
If your sole goal is to increase flexibility and range of motion, you’ll need to do yoga at least two times per week. If you want certain parts of your body to become more flexible (for instance, your hamstrings or lower back), you’ll need to hold a static, relaxed stretch with that specific part of the body for at least five total minutes a week. You could hold the stretch for 2.5 minutes in two different sessions or 5 minutes in one session.(4) Yin yoga is one type of yoga that involves long-hold, relaxed static stretches.
Are you getting started with a yoga journey?
Read our guide, Yoga for Beginners.
2. Yoga As A Complement To Other Styles of Fitness
For people who already exercise frequently, yoga may not significantly impact strength or cardiovascular health. But it can make your other training sessions better. Here’s how.
Yoga For Injury Avoidance
As discussed in our blog post about yoga for back pain, yoga is a scientifically-proven way to relieve back pain related to injury or chronic pain.(5) A regular yoga practice may make your back healthier overall, reducing the risk of back injury in other sports.
A lack of balance often causes blunt force injuries in sports. Yoga helps you to become more balanced, potentially helping avoid trips, falls, or collisions.(6) Tripping over dumbbells is one of the most common gym-based injuries. Yoga can help! (As can properly re-racking your weights, but gym etiquette deserves its blog post…)
Yoga For Body Awareness
Yoga increases general body awareness. Knowing where our body is in space is called kinesthetic awareness. Knowing where it is in relation to itself is called proprioception. These skills are critical components of effective movement. When we have a natural awareness of where our body is, we ensure better form and function. Body awareness helps us feel if our deadlift form is proper, how high to lift a knee when climbing stairs, and if our shoulders are over our elbows in plank. When you practice yoga, you’ll learn enough about your body to make the rest of your workouts more targeted and effective. Flexibility, coordination, and mobility are all skills learned in yoga to make the rest of your activities more effective.
Interestingly, scientists have found that yoga reduces inflammation in the body, but they don’t understand why. Some posit that it’s due to body awareness; something about feeling very connected to one’s body serves as a natural anti-inflammatory.(7)
Yoga For Mobility
Flexibility occurs when a muscle expands in a passive, usually static position. Mobility is a group of muscles’ ability to expand integrally while in motion. Mobility is dynamic and active eccentric muscle contraction, whereas flexibility is passive and eccentric.(8) Mobility is the ability to move in and out of stretches with grace and sometimes with force. Less intense styles of yoga, like Yin yoga, help with flexibility. More movement-focused styles of yoga, like Vinyasa and Ashtanga, help with mobility.
Interestingly, both passive yoga and more mobility-focused yoga help release muscle tension. Mobility training stimulates the nerves that contract muscles while lengthening them and the tissues surrounding them (i.e., fascia). Blood flow increases to the mobilized space, joint range of motion increases, and tension subsides.(9) Because the movements are controlled and span multiple body parts, yoga builds coordination and an intrinsic understanding of stabilization.
Yoga for Athlete’s Recovery
Flexibility training that involves holding passive stretches (like yoga) can reduce sensations caused by the nervous system in that area. In other ways, yoga can help make physical feelings of soreness, pain, and burn to subside. That’s one reason why many athletes save yoga for after a training session, especially if muscles are inflamed or sore.(10)
3. Yoga For Mental Health: A Mind-Body Exercise
Yoga is proven to have more beneficial mental health impacts than other kinds of exercise.(11) You won’t burn as many calories as a run or build as much muscle as a barbell strength workout. But you will exercise your mind-body connection in a yoga class, and this may be the greatest exercise of them all.
Yoga For Positive Psychology
Stretching is proven to decrease cortisol levels in the body and has positive psychosocial outcomes, whether you do it independently or in a group class.(12) Women, in particular, are less likely to objectify themselves and less likely to suffer from an eating disorder when they practice yoga.(13)
Yoga: A Mindfulness Phenomenon
While mindfulness is a term thrown around often in popular culture, it carries actual psychological benefits. Mindfulness is a quality of non-judgmental, observational focus on one’s current experience. Being mindful means feeling curious, experiential, open, and accepting of one’s current state. Mindful people are proprioceptive and interceptive; they use their senses to interpret their bodies and their world. Very mindful people become more in-tune with their interpretations, beliefs, memories, conditioning, attitudes, and affect on the planet.
Yoga is considered a mind-body therapy that teaches the practitioner mindfulness. Yogis often feel more confident in their public and private interactions. Scientists who study yoga even call it a “mindfulness phenomenon.”(14)
How Does Yoga Help You To Stay Fit?
If you’re getting started with or back into exercise, yoga will help you build muscle and cardiovascular health. If you already work out, yoga can complement your current training, making it more effective and less likely to cause injury. Finally, yoga helps everyone stay mentally fit.
,